A mirroring template refers to the runtime environment of a cloud server instance, including configurations such as the operating system and pre-installed software. Baidu Cloud provides a dedicated public image for each FPGA instance by default, allowing users to choose the most suitable image type based on their specific needs.

Based on Baidu Cloud’s self-developed FPGA acceleration card, a complete set of FPGA standard development environment is provided. Users can utilize the image toolkit offered by Baidu Cloud to develop and debug their own business functions on the FPGA or migrate existing modules to the FPGA accelerator card.
The self-developed FPGA accelerator card from Baidu uses the Xilinx 20nm KU115 FPGA. The FPGA board features four DDR4 channels, with 72 bits per channel, ECC support, 2GB capacity, and operates at 2400MHz. The FPGA is connected to the CPU via PCIe 3.0 x8. The block diagram of the board is as follows:
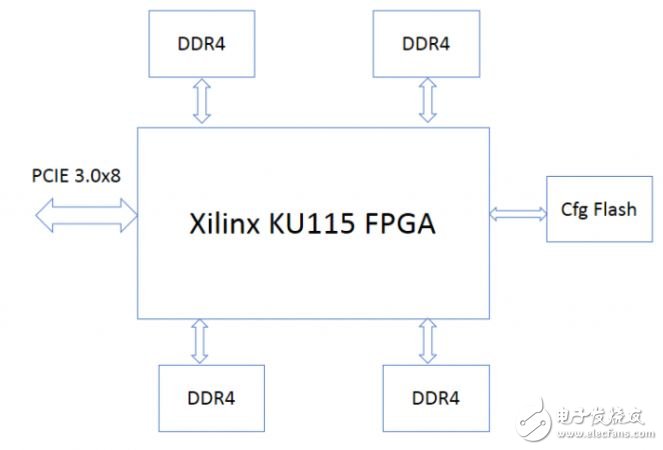
Based on this FPGA board, Baidu also offers a comprehensive standard development environment. The system architecture is shown below:
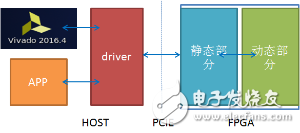
The FPGA standard development environment is highly flexible:
You can develop the dynamic part of the FPGA logic, which includes most of the resources of the KU115 chip and the four DDR4 channels, enabling full customization of the FPGA circuit.
Baidu Cloud provides drivers and reference designs for applications, allowing you to modify the driver and application software side to call the FPGA for specific tasks.
You can directly use the toolkit provided by Baidu to replace the dynamic logic of the FPGA.
The environment also includes a virtual JTAG tool that allows debugging using Vivado.
The FPGA standard development environment is divided into two parts:
FPGA Software Driver Development
Taking an example program that runs the PE (Processing Element) for simple floating-point vector addition, the process includes:
1. Compiling the driver and providing a sample program for compilation.
2. Running the sample program.
FPGA Logic Development
Develop and debug user logic using the provided toolkit:
1. Compile your dynamic logic with Baidu_HW_design_toolkit.
2. Replace your dynamic logic using bin_pr_tools.
3. Debug your dynamic logic using Vivado.
FPGA Software Driver Development
Compiling the Driver
Modify the KERNELDIR variable in the driver/Makefile to point to the current kernel build directory, typically /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/build or /usr/src/kernels/$(uname -r).
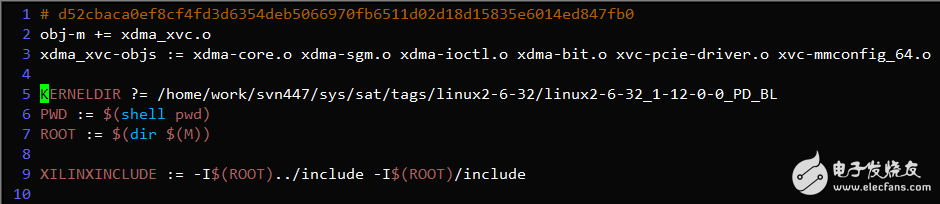
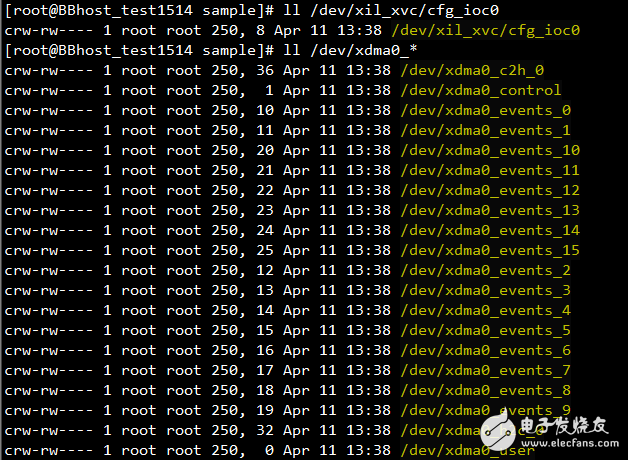
Run 'make'. If the compilation is successful, the xdma_xvc.ko driver file will be generated in the current directory, as shown below:
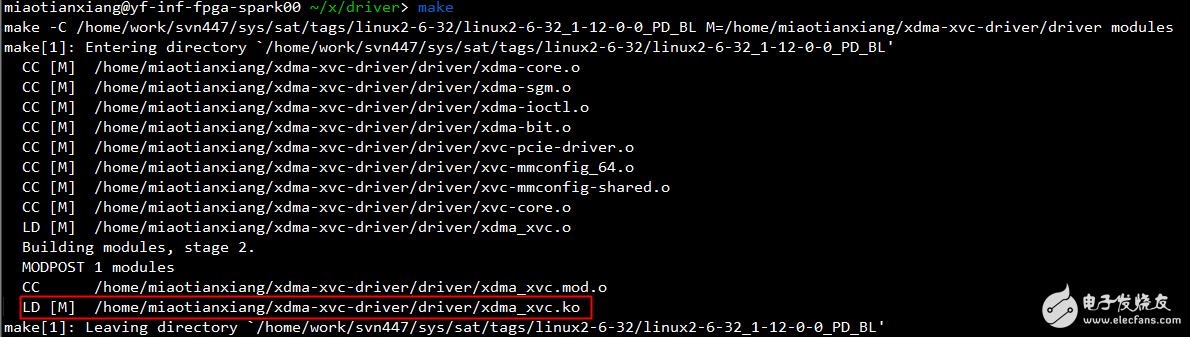
Use 'insmod xdma_xvc.ko' to load the driver. A device file named /dev/xil_xvc/cfg_ioc0 should appear in the /dev directory.
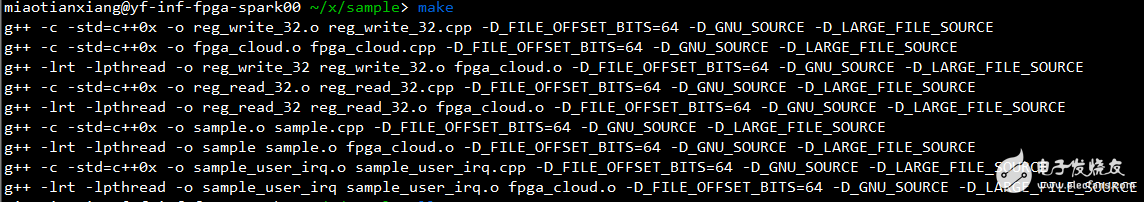
Navigate to the sample directory and run 'make'. If successful, executable files like sample and sample_user_irq will be generated, as shown below:
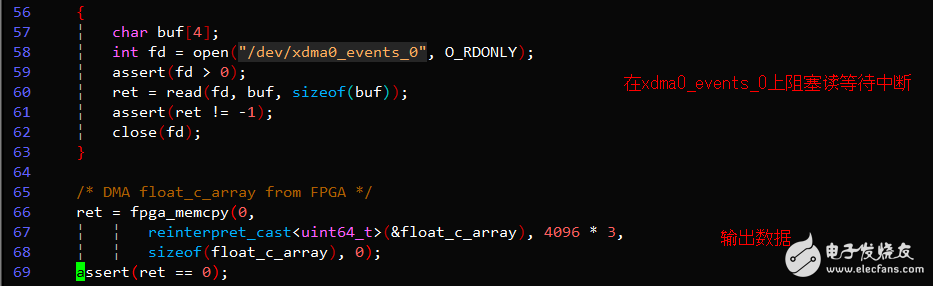
Execute './sample' to see the result. The PE correctly performs the floating-point vector addition function. The sample uses a polling register method to check if the command is completed.
Run './sample_user_irq' to see another result. This version uses interrupt mode to check the completion status.
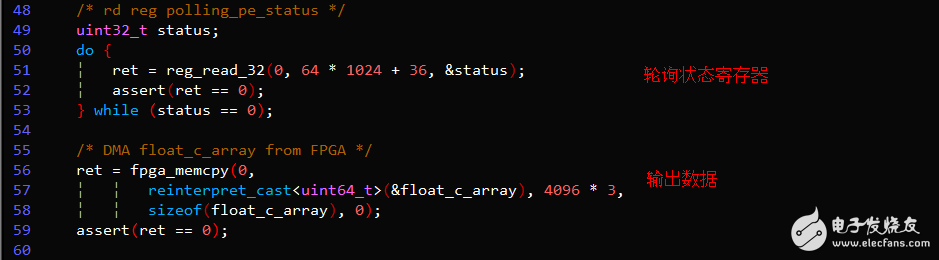
Key Code Example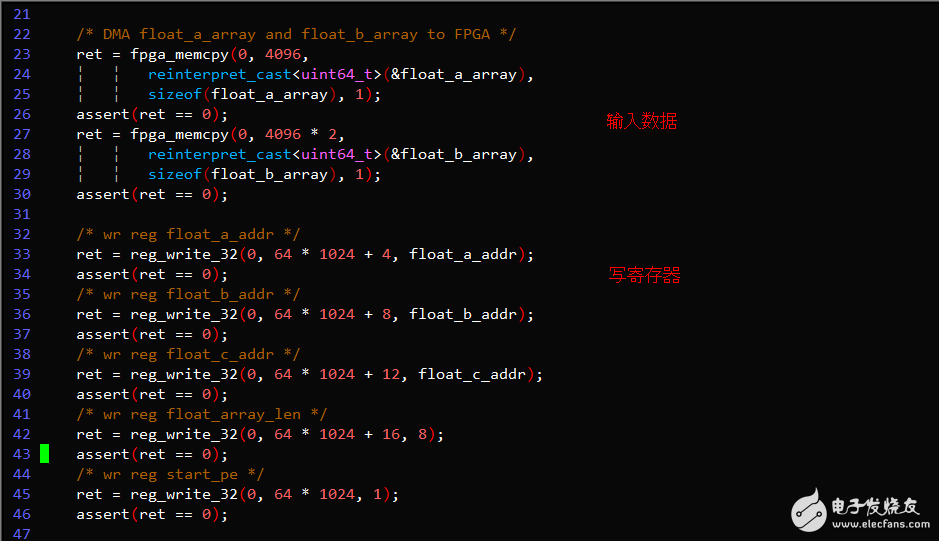
YIWU JUHE TRADING COMPANY , https://www.nx-vapes.com