Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) is a combination of three technologies: sensor, communication and computer. It is difficult for wireless sensor networks to integrate the logical information world with the objective physical world, changing the way humans interact with nature. Wide application prospects. Wireless sensor networks have many characteristics that are different from traditional networks, such as severely limited energy and frequent changes in topology. Therefore, the design of the WSN network protocol is quite different from the design of various existing network protocols, and thus faces various new challenges. Among the many protocols in the protocol stack, the network layer routing protocol algorithm has become a hot research topic as a key technology.
2 Routing protocol for wireless sensor networks
Since there are many classification standards for WSN routing protocols, the classification methods of routing protocols are also diverse. The routing protocols are divided into two types according to different working principles of the routing protocol, and each type of typical routing protocol is analyzed.
2.1 Plane routing
Planar routing considers that each node in the sensor network has the same function and equal role. The node either actively reports its own event detection result to other nodes, or other nodes send query information to the node that detects the event, and the data transmission passes through multiple nodes. The multi-hop routing cooperative forwarding is completed. The Sensor Negotiation Sensor SPIN (Sensor Protocols for InformaTIon via NegoTIaTIon) is the first data-centric algorithm in planar routing, which reduces data redundancy and energy loss through a node negotiation mechanism. SPIN is a data-centric routing algorithm based on negotiation mechanism. SPIN firstly abstracts the characteristics of the data received by the node to form a meta-data describing the characteristics of the data received by the node. Before forwarding the received data, node A first negotiates with neighboring Node B using metadata, and sends an ADV signal to determine whether Node B needs the data (Fig. 1a). If Node B has a demand for the data represented by the metadata, a feedback signal REO (Figure lb) is issued. Otherwise, the ADV signal is discarded, and then node A forwards the data DATA to node B (Fig. lc). After receiving the data forwarded from node A, node B adopts the same processing method as node A. The metadata is first negotiated with all nodes connected to it to see if the data is needed, and the ADV signal is sent (Fig. 1d). If the node has a demand, it will reply to the REQ signal. If there is no demand, the ADV signal will be directly discarded (Fig. 1e), and then Node B will send the data DATA to all nodes that reply to the REQ signal (Fig. 1f).

The SPIN algorithm does not explicitly define the format of the metadata. The specific format and application related, such as the format of ADV and REQ, can be specified according to the specific application. In addition, when the topology changes, each node only needs to maintain the state of its neighbors in a local scope, without the need to broadcast the whole network, saving energy and reducing the computing power of the node. This SPIN is called SPIN. -1. However, SPIN-1 cannot guarantee the correct delivery of remote data. For example, the remote node needs data and the near-end node adjacent to the source node does not need it. At the beginning of the forwarding, the metadata representing the data is discarded, and no REQ reply is made. , causing data delivery to fail. In order to solve this problem, SPIN-2 added an energy threshold mechanism based on SPIN-1. The energy of the neighboring node is detected before the data is delivered. If the energy value is below a certain threshold, the node is considered to be insufficiently capable of completing the remote delivery task, and the data is forwarded to other neighboring nodes with sufficient energy. In addition, for different application scenarios, SPIN's other extended protocols, such as SPIN-BC and SPIN-RL, are dedicated to traditional peer-to-peer networks for sensor networks such as multicast networks, SPIN-PP and SPIN-EC. optimization.
2.2 Hierarchical routing
Hierarchical routing (also known as cluster-based routing) is the first to be generated and applied to wired networks to meet the efficient communication of large-scale networks. Therefore, the concept of hierarchical routing has also been introduced into the WSN to meet the low-energy and high-efficiency communication of sensor nodes. In hierarchical routing, high-energy nodes can be used in high-energy applications such as data forwarding, data query, data fusion, remote communication, and global route maintenance; low-energy nodes are used for low-energy applications such as event detection, target location, and local route maintenance. Application. In this way, different applications are reasonably allocated according to the different capabilities of the nodes, so that the nodes can fully utilize their respective advantages to cope with large-scale network conditions and effectively improve the lifetime of the entire network. Hierarchical routing mainly includes two levels of routing: one is for selecting cluster head nodes, and the other is for routing. LEACH (low-energy adapTIveclustering hierarchy) is an early WSN hierarchical routing algorithm based on clustering idea. Compared with the traditional network fixed gateway node, the energy of the node in the WSN is limited, so the same cluster head node cannot be used as the gateway. LEACH randomly selects a few nodes from the WSN as cluster heads. Considering the balance of energy consumption of each node in the network, let other nodes that have not done cluster heads take turns as cluster heads, so that the network will not be exhausted due to the lack of energy of a few nodes. Network 瘫痪.
The LEACH algorithm is divided into two stages: cluster head establishment and steady state. The former is the key to LEACH algorithm implementation, and the latter is the guarantee of data transmission. In the cluster head establishment phase, the node randomly selects a value r (O
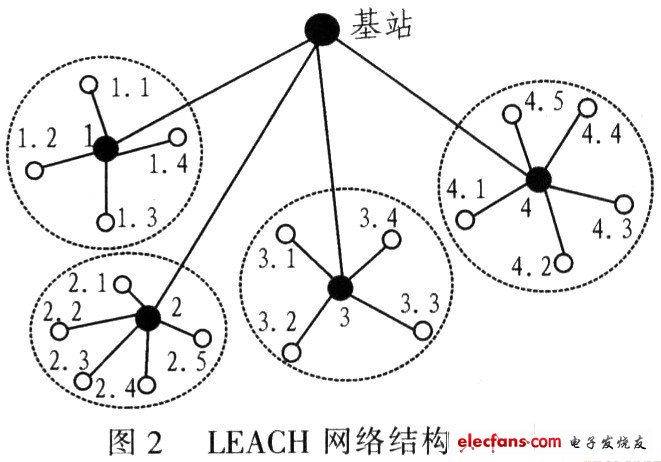
LEACH's clustering mechanism can reduce the overall energy consumption of the network and prolong the network lifetime; TDMA coding is used between nodes in the cluster, CDMA coding is used between the cluster head and the base station to ensure effective information transmission; data acquisition and cluster head nodes are Periodically, the network is suitable for monitoring continuous change events.
3 Conclusion
The network layer of the wireless sensor network is expounded. The routing algorithm is used as the research main line to deeply analyze the two routing algorithms of WSN. The research of routing algorithm mainly has the following problems: (1) Data fusion at the network layer or application layer, the network layer mainly relies on routing algorithm coordination to discard redundant packets, reduce node energy consumption and improve data forwarding efficiency. (2) To ensure the reliability of data transmission and minimize the overhead of multipath maintenance, the algorithm should not be too complicated. (3) For WSN, in addition to considering the situation when the node is stationary, node mobility also needs to be considered. If it is not a mobile tracking node, it is generally possible to turn off the RF channel when the node moves. (4) The routing algorithm should handle the coordination between nodes, even if the number of nodes is large, normal data forwarding can be completed, and will not cause failure in a short time. (5) For WSNs with a large number of nodes, due to the randomness of network topology distribution, some key nodes may consume more energy, while other nodes consume less energy and the network load is unbalanced. Therefore, it is necessary to use the Lunan algorithm to enhance network load balancing. (6) Due to the particularity of the WSN, the energy consumption of the nodes must be considered. Therefore, to study the WSN routing algorithm, it is necessary to reduce the node energy consumption as much as possible to prolong the network lifetime.
Spin dryers are very common in every family. Banshen spin dryers, with high quality, good design and best service. Many products have been sold to over 30 countries. After many years of developing, banshen spin dryers are getting better and better.
Our well-equipped facilities and excellent quality control throughout all stages of production enable us to guarantee total customer satisfaction. Besides, we have received CE, CB, RoHS and CCC certifications.
As a result of our high quality products and outstanding customer service, we have gained a global sales network reaching America, Asia, Europe, Africa, the Middle East and other countries and regions.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a custom order, please feel free to contact us. We are looking forward to forming successful business relationships with new clients around the world in the near future.
Big Capacity Spin Dryer,Top Loading Clothes Dryer,Top Load Washer And Dryer,6.5Kg Top Loading Spin Dryer
Ningbo Banshen Electric Appliance Co., Ltd , https://www.banshendq.com